In today’s interconnected world, small businesses are increasingly becoming prime targets for cybercriminals. Many attackers see small businesses as low-hanging fruit—often lacking the robust defenses of larger organizations. To safeguard your business, it’s crucial to understand the leading causes of cybersecurity breaches and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
Let’s dive into the top ten causes of small business cybersecurity breaches and explore actionable steps to protect your operations.
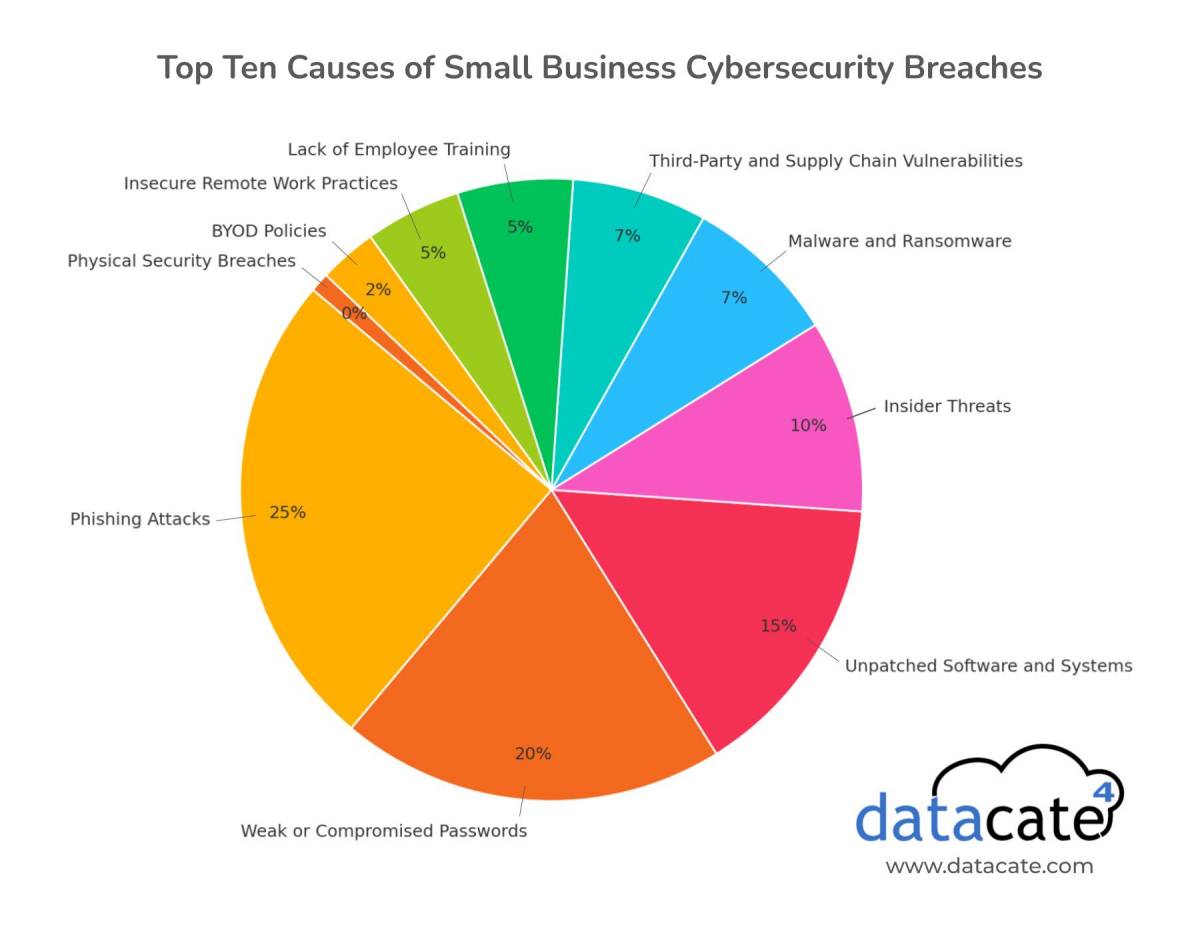
1. Phishing Attacks: The Leading Cause
Phishing is the most common method attackers use to breach small businesses. Cybercriminals trick employees into sharing sensitive information like passwords or financial data by sending fraudulent emails or messages that appear to come from trusted sources.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Train employees to recognize phishing attempts.
- Implement email filtering tools.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add a layer of security.
2. Weak or Compromised Passwords
Simple, easily guessed passwords or reusing credentials across multiple accounts can leave your business vulnerable. Once compromised, these credentials are often sold on the dark web.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Enforce strong password policies.
- Require employees to use a password manager.
- Regularly update passwords and avoid reusing them.
3. Unpatched Software and Systems
Hackers exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. Failing to update or patch your systems is an open invitation for attackers.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Schedule regular updates for all software and operating systems.
- Enable automatic updates where possible.
- Conduct routine vulnerability assessments.
4. Insider Threats
Not all threats come from outside the organization. Whether malicious or negligent, employees can cause breaches by mishandling data or intentionally leaking information.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Limit access to sensitive data based on roles.
- Monitor user activity and implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions.
- Create clear policies for handling confidential information.
5. Malware and Ransomware
Malware and ransomware attacks are on the rise, often delivered via phishing emails or malicious downloads. These attacks can encrypt your data, holding it hostage until a ransom is paid.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Deploy robust endpoint security solutions.
- Educate employees about safe downloading practices.
- Back up data regularly and store backups securely.
6. Third-party and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Small businesses often rely on third-party vendors for tools and services, but your business can also be affected if a vendor’s security is compromised.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Vet third-party vendors for strong security practices.
- Require contractual agreements for cybersecurity standards.
- Regularly audit vendor access to your systems.
7. Lack of Employee Training
Even the best security tools are ineffective if employees don’t understand cybersecurity basics. Many breaches occur due to simple mistakes, such as clicking suspicious links.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Provide regular cybersecurity training sessions.
- Simulate phishing attacks to test employee readiness.
- Foster a culture of security awareness.
8. Insecure Remote Work Practices
The shift to remote work has expanded the attack surface for many businesses. Unsecured Wi-Fi networks, personal devices, and poorly configured remote access tools are common weak points.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Use a virtual private network (VPN) for secure connections.
- Require company-approved devices for remote work.
- Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.
9. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Policies
Allowing employees to use personal devices for work can increase convenience but also introduces significant security risks, especially if these devices aren’t properly secured.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Develop a strict BYOD policy.
- Require device encryption and antivirus software.
- Separate work and personal data on devices.
10. Physical Security Breaches
Not all threats are digital. Lost or stolen devices, as well as improper disposal of sensitive documents, can lead to breaches.
How to Protect Your Business:
- Use encryption for all company devices.
- Implement secure disposal practices for physical documents.
- Require employees to report lost or stolen devices immediately.
Taking Action
While the causes of cybersecurity breaches vary, the common thread is that most are preventable. You can significantly reduce your risk by implementing strong security measures, training your employees, and leveraging reliable tools and services.
Datacate specializes in providing secure, scalable IT solutions tailored to small businesses. From endpoint protection to data backup and disaster recovery, our services help you build a robust defense against cybersecurity threats.
Don’t let cyber risks keep you up at night—contact Datacate today to learn how we can help secure your business.
References
Cyberattacks are on the rise, and that includes small businesses. Here’s what to know
35 Alarming Small Business Cybersecurity Statistics for 2024
Cybersecurity Stats: Facts And Figures You Should Know




